The cavum septi pellucida (CSP) is a closed cavity in the brain, located on the midline of the transverse plane between the two leaves of the septum pellucidum, which separate the lateral ventricle (1,2) It is thought to arise due to cavitation of the inferior aspect of the commissural plate, presumable around 17 weeks of gestation (3)In fact, for well over a decade, assessment of the CSP has been considered part of the required elements of a standard examination of fetal morphology in guidelines developed by multiple specialty societies Our objective is to present the 4 reasons why all practicingThe cave of septum pellucidum (CSP), cavum septi pellucidi, or cavity of septum pellucidum, is a slitlike space in the septum pellucidum that is present in fetuses but usually fuses during infancy The septum pellucidum is a laminated thin translucent vertical membrane in the midline of the brain separating the anterior horns of the right and left ventricles

Dedicated To The Mission Of Bringing Free Or Low Cost Educational Materials And Information To The Global Ultrasound Community
Absent cavum septum pellucidum ultrasound images
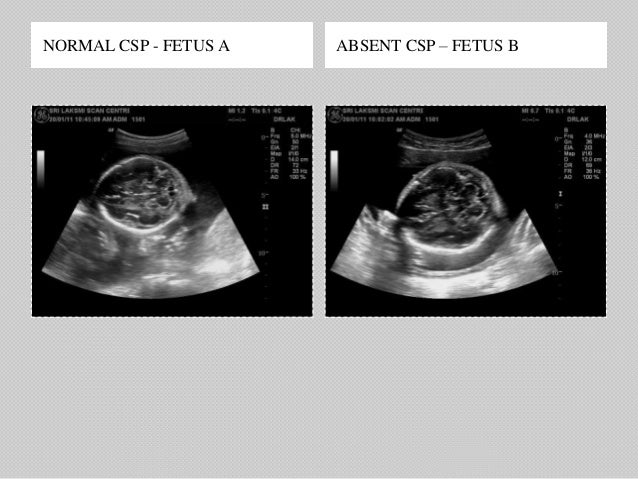
Absent cavum septum pellucidum ultrasound images-Cephaly defect on the right (Fig 6) The CSP was absent, as well as the corpus callosum Figure 5 Patient 5 (a) Axial US image obtained through the brain shows absence of the CSP (arrow) A small schizencephalic defect was not identified at initial prenatal US (b) Comparison US image of an infant who was normal at birth shows a slightlyAbsent CSP – fused anterior horns;




Fetal Central Nervous System Anomalies Chapter 6 Fetal Medicine
Thus, if the CSP is not seen with certainty on standard axial images, obtain a series of coronal images, and also attempt to identify the CC directly with a midsagittal view9 428 J Ultrasound Med 10;Jun 01, 19 · Ultrasound is the preferred method for screening the fetal central nervous system (CNS) It is a safe, costeffective, and repeatable realtime modality The cavum septi pellucidi (CSP) is a key structure in fetal brains, serving as an anatomic landmark inJun 11, 12 · INTRODUCTION The cavum septi pellucidi (CSP) is an important landmark in evaluation of the fetal brain and has become integral to both routine and detailed ultrasound examinations 1Development of the CSP begins at c 10–12 weeks and it is fully formed by 17 weeks of gestation 2According to Rakic and Yakovlev 3, the anterior commissure and the septal area
Feb 11, 17 This Pin was discovered by Lil Lima Discover (and save!) your own Pins onJul 07, 19 · Ultrasound The corpus callosum can be shown with ultrasound (US), but some degree of technical skill is required because it is not apparent in the standard axial planes, and additional coronal and particularly sagittal planes are required complete ACC is commonly associated with a hypoplastic or absent cavum septi pellucidi (CSP) Fig 343D fetal CNS evaluation with tomographic ultrasound imaging (TUI) The absence of CSP is indicated by the red circle in cases with severe brain anomalies holoprosencephaly and
MRI of the fetal corpus callosum with tractography a step beyond ultrasound Houman Mahallati1, Neil O'Gorman1, Laurent J Salomon1, David Grevent2, AnneElodie Millischer2 The corpus callosum develops from 7 weeks' gestation and is completely formed by weeks It develops in four sections, starting with the anterior genu, then the bodyAbove This is the same acquisition plane for the BPD and HC Visualization of the thalami, the midline falx, and the boxlike cavum septi pellucidi (CSP) are possible The presence or absence of the CSP is a key factor in defining abnormal brain anatomy BPD Measurements Measurement Planes 1 The BPD can be measured through any plane thatMay 28, · CNS structures evaluated during a basic fetal ultrasound examination include lateral ventricles, choroid plexuses, cavum septi pellucidi, falx, thalami, cerebellum, cisterna magna, and spine Their appearance in transthalamic, transventricular, and transcerebellar planes is shown in the following images ( image 1 and image 2 and image 3 )




Abnormalities Of The Fetal Central Nervous System Prenatal Us Diagnosis With Postnatal Correlation Radiographics




Complete Agenesis Of The Corpus Callosum Cacc The Most Common Commissural Anomaly Diagnosed Prenatally Is Often Suspected On Fetal Ultrasound When The Cavum Septi Pellucidi Csp Is Absent And Additional Signs Such
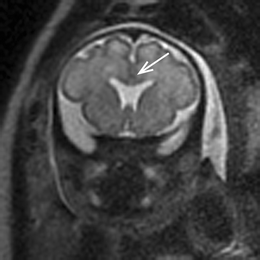
A, Coronal true fast imaging with steadystate precession (FISP) or fast imaging employing steadystate acquisition (FIESTA) image of brain from fetal MRI performed of fetus at 31 weeks 6 days' gestational age confirms ultrasound (US) finding (not shown) of complete absence of cavum septi pellucidi (CSP) No additional abnormalities are identifiedSelected ultrasound images are shown There was normal fetal biometry The corpus callosum was identified The CSP however could not be clearly seen There was bilateral renal pyelectasis (not shown), but otherwise normal anatomySecondtrimester sonographic images of the brain;



Http Www Oyg Com Co Files The Cavum Septi Pellucidi Pdf




Pdf Non Visualisation Of Cavum Septi Pellucidi Implication In Prenatal Diagnosis
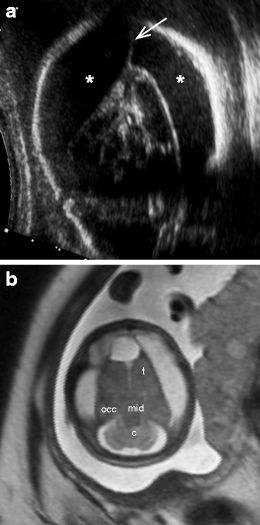
Coronal transvaginal image The absence of the CSP may be due to either a developmental anomaly or a secondary disruption Failure to visualize the CSP on the standard transaxial image between 18 and 37 weeks' gestation should alert the sonologist to the possibility of agenesis of the corpus callosumEpidemiology The septum pellucidum is partly or entirely absent in 2 or 3 individuals per 100,000 in the general population Pathology An absent septum pellucidum may be developmental or acquired secondary to another pathological process 1,2 Cavum septum pellucidum is always visualized between 18 and 37 weeks and within a biparietal diameter of 44 to mm Failure to30T MRI results were 44 cases of CSP, 1 case of misdiagnosis, and 1 case of missed diagnosis



Midline Anomalies Of The Brain




Absent Cavum Septi Pellucidi American Journal Of Obstetrics Gynecology
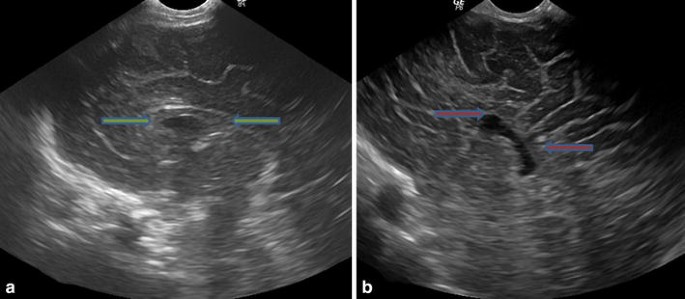
Fig 1—Normal cavum septi pellucidi (CSP) on fetal ultrasound (US) and fetal MRI of same patient and postnatal MRI of different patient A, Fetus at 26 weeks 2 days' gestational age Axial US image obtained at level of paired thalami clearly shows leaves of CSP (arrows) in continuation with medial walls of frontal horns of lateral ventriclesJun 06, · This increase in rate of CSP detection may also be due to improvements in image quality of transvaginal ultrasound as well as the increasing use of transvaginal POCUS This uncommon condition was first described by Larsen and Solomon in 1978, with only 19 additional cases documented until 01 7, 8 It now accounts for nearly 5% of all ectopicBackground Cavum septi pellucidi (CSP) is easily evaluated in the second and third trimester of the pregnancyThe structure is an important feature of the standard planes used for routine morphological assessment of fetal head and central nervous system (CNS) transthalamic and transventricular plane




Absence Of The Cavum Septum Pellucidum Iame



Fetal Head The Obg Project
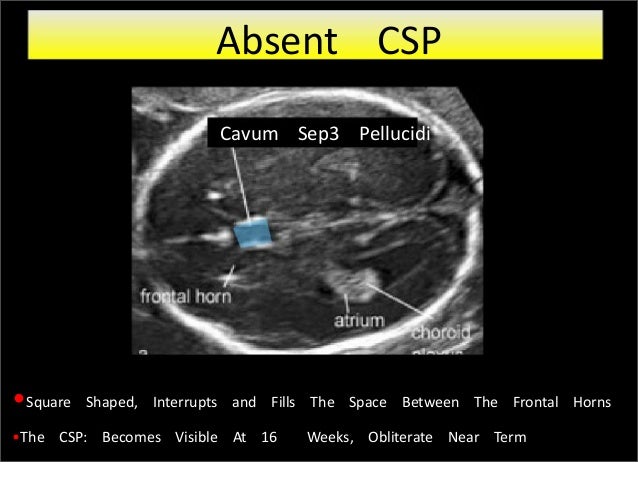
These US exams all suggested an absent or abnormal CSP, without additional findings Of the 27, 15 also showed an absent/abnormal CSP on fetal MRI, and 12 were found to have a normal CSP on fetal MRI The positive predictive value of ultrasound in identifying an isolated anomaly of the CSP was 056 (15/27) The false discovery rate was 044 (12Fetuses With Abnormal Cavum Septi Pellucidi J Clin Gynecol Obstet 16;5(4) The absence of CSP in the second and third trimester has been associated with ACC, septooptic dysplasia, hydranencephaly, porencephaly, schizencephaly, holoprosencephaly, syntelencephaly or severe chronic hydrocephaly 110, 14Oct 05, 18 · CSP PLEASE INSERT FIGURE 3 Caption Cavum Septum Pellucidum (CSP) and Corpus Collosum Never clear a fetal head ultrasound without seeing a CSP CSP box should always be clear without a bisecting line down the middle An abnormal CSP is a marker for abnormal forebrain development




Dedicated To The Mission Of Bringing Free Or Low Cost Educational Materials And Information To The Global Ultrasound Community




Absence Of The Cavum Septum Pellucidum Iame
Chromosomal anomalies include trisomy 18, 8 and 13 Ultrasound protocol Name Scanning technique Explanation Axial head Axial head through the thalamus and CSP Presence or absence of CSP (make sure that this is a box like structure and not the medial walls of the ventricles) Axial head – ventriclesApr 18, 17 · Nine patients were identified as having a prominent cavum septi pellucidi, and 6 were identified as having a prominent cavum vergae The mean gestational age ± SD was 227 ± 59 weeks Eleven patients made it to delivery Of the 15 patients, 4 were thought to have trisomy 21, and 13 had congenital anomalies Outcomes included 10 major adverseJan 07, 15 · Ultrasound images of cavum septi pellucidi (CSP) in two fetuses with partial agenesis of the corpus callosum at 31 weeks' gestation, one with abnormal shape of CSP (a) and one with normal shape of CSP (b)




This 25 Weeker Anjali Ultrasound Colour Doppler Centre Facebook




3d Fetal Cns Evaluation With Tomographic Ultrasound Imaging Tui The Download Scientific Diagram
Objective The cavum septi pellucidi (CSP) is routinely imaged in the fetal brain during obstetric sonography;Jun 25, 14 · The absence of CSP in most cases is associated with neuroanatomical anomalies that include agenesis of the corpus callosum, schizencephaly, septooptic dysplasia, holoprosencephaly, chronic hydrocephalus and acquired fetal brain injury Fetal brain MRI scan will help in proper diagnosis if CSP is not visualized in follow up scans alsoJan 03, 16 · Thomas C Winter, MD Time 29 min About This Lecture In this obstetrics lecture, the speaker discusses normal anatomy and pathology of the septum cavum pellucidum , as well as imaging pitfalls Upon completion of this educational activity the participant will be able to analyze a cavum septum pellucidum ultrasound image and




Dedicated To The Mission Of Bringing Free Or Low Cost Educational Materials And Information To The Global Ultrasound Community




Corpus Callosum And Septum Pellucidum Anomalies Sciencedirect
Oct 23, 14 · Charcharox Posted I just came back from my 21 weeks ultrasound scan and the dr who scanned me told me that my baby brain CSP (cavum septum pellucidum) is absent She said she doesn't know anything about it and can't tell me anything She refered me to a neurologist for next week and I don't know how I can cope with such long wait!The cavum septi pellucidi is critical to the diagnosis of a number of CNS malformations 4 The presence of the CSP excludes complete agenesis of the corpus callosum while the absence of the CSP suggests the possibility of a number of other intracranial abnormalities, including septoMar 01, 10 · The cavum septi pellucidi (CSP) is routinely imaged on views of the fetal brain obtained during obstetric sonography Assessment of the CSP is considered part of the minimum elements of a standard examination of fetal anatomy in guidelines developed by the American Institute of Ultrasound in Medicine in collaboration with the American College of Radiology and




The Cavum Septi Pellucidi Winter 10 Journal Of Ultrasound In Medicine Wiley Online Library




Absent Cavum Septum Pellucidum Ultrasound Medical Ultrasound Obstetric Ultrasound
•Absence of the normal cavum septi pellucidi (CSP) during the routine anatomical survey using axial scan •May be indicative of a HPE, AGCC or SOD Normal CSP Absent CSP •3D ultrasound can help image the optic nerves Isolated ASP vs SOD Evaluating the Optic Nerves & Chiasma Tough Diagnosis Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 11;Feb 03, 14 · After completing this course, the participant should be able to Understand the embryologic development of the cavum septum pellucidum Review the differential diagnosis for an absent cavum septum pellucidum Identify the sonographic signs associated with agenesis of the corpus callosum Discuss the neurologic outcome for an isolated absence ofThis second trimester fetus shows all the features of alobar holoprosencephaly The 3D ultrasound images of the fetal face show absence of the nose or arhinia In addition, there is a rudimentary single eye seen lower down in the midline This is known as cyclopia and the fetus is said to be a cyclops



Fetalmedicine Org Var Uploads 18 23 Weeks Scan Pdf




Free Chapter Normal Fetal Ultrasound Biometry Ob Images
The location of a cavum septum pellucidum (CSP) within the lateral ventricles (LV) and above the septal area (S) on a frontal section of the human brain CSP, delimited by green lines, is a marker of abnormal forebrain development Figure 74 is a copy of Figure 71, except that in Figure 71 a typical septum pellucidum (SP) is shown, whileApr 15, 21 · Among these patients, 2 of whom were trophoblastic diseases, 5 were pregnancy abortion, 8 were cervical pregnancy, and 45 were CSP (2) The results of ultrasound detection were 37 cases of CSP, 7 cases of misdiagnosis, and 8 cases of missed diagnosis;Anencephaly is the most severe form of cranial neural tube defect (NTD) and is characterized by an absence of cortical tissue (although the brainstem and cerebellum may be variably present) as well as an absence of the cranial vault The morpholo Danielle4567 OB/Gyn Utrasound 301 Mod 4




Figure 2 From Absent Cavum Septum Pellucidum A Review With Emphasis On Associated Commissural Abnormalities Semantic Scholar




Lobar Holoprosencephaly Absent Csp Present In 100 Of Cases Ultrasound Technician Medical Ultrasound Obstetric Ultrasound
Jan 25, 11 · Images 9,10 MRI images of the fetal brain Image 9 shows a normal optic tracts, this excludes septooptic dysplasia Image 10 shows a coronal view of the brain, note a missing cavum septum pellucidum Images 11,12 Images show an axial view of the fetal brain, note absent cavum septum pellucidum, the frontal horns are squared–444 The Cavum Septi Pellucidi Why Is It Important?Name of anomaly Absent CSP, complete or partial Findings CSP not see on axial image, develops from front to back, hence the anterior part maybe seen, but posterior part may be absent, Colpocephaly – enlargement of the occipital portion of the lateral ventricle (AKA teardrop sign), high riding third ventricle




Ch 5 Ultrasound In The Second Trimester Brian S Radiology Learning Diary




Scielo Brasil Ultrasonographic Evaluation Of The Fetal Central Nervous System Review Of Guidelines Ultrasonographic Evaluation Of The Fetal Central Nervous System Review Of Guidelines
Absent cavum septi pellucidi and teardrop configuration of the lateral ventricles with possible ventriculomegaly Antenatal diagnosis is based upon the nonvisualization of the corpus callosum at transfontanellar ultrasound in either the sagittal or the coronal plane8,9 More subtle findings, such as hypoplasia and partialAbsent cavum septi pellucidi Prenat Diagn 18;38(6) 14 GarcíaArreza A, GarcíaDíaz L, Fajardo M, Carreto P, Antiñolo Obesity impairs the quality of ultrasound images All3D ultrasound examination and the corpus callosum 171 Table 1 Successful visualization of the corpus callosum after appropriate sectioning of the threedimensional volume of the head according to the initial plane of acquisition Corpus callosum Acquisition plane n Seen (%) Appearance Midsagittal with rotation of 0–179 from the direction of the nose (0 ) 72 67 (93)




The Cavum Septi Pellucidi Winter 10 Journal Of Ultrasound In Medicine Wiley Online Library



Www Pedrad Org Linkclick Aspx Fileticket Hjoixsgmuvi 3d Portalid 5
Ultrasound Of Callosal Agenesis The corpus callosum is a thin band of white matter, which is difficult to demonstrate sonographically It is only well visualized on midsagittal or midcoronal views of the brain and requires optimal angles of insonation to demonstrateAug 10, 16 · Cavum septi pellucidi (CSP) should be the landmark for measurement of biparietal diameter and head circumference Coronal images also helpful if fetal head position makes correct axial plane difficult CSP seen between frontal horns inferior to corpus callosum Cavum septi et vergae is an anatomic variant that may cause confusionThe cavum septi pellucidi was present and visible at least in part in 17 (63%) of the 27 pACC examinations In nine of the 27 (333%) pACC examinations, there was neither ventriculomegaly nor absence of the cavum septi pellucidi Associated anomalies were present in 25/54 (463%) cases, and in 11 these included or consisted of CNS abnormalities



Non Visualisation Of Cavum Septi Pellucidi Implication In Prenatal Diagnosis Insights Into Imaging Full Text




Corpus Callosum And Septum Pellucidum Anomalies Sciencedirect
Emergency Ultrasound Standard Reporting Guidelines Contributors to the 18 Emergency Ultrasound Standard Reporting Guidelines Rachel B Liu, MD, FACEP, Chair, ACEP Emergency Ultrasound Section Mike Blaivas, MD, FACEP, ACEP member atlarge Chris Moore, MD, FACEP , ACEP member atlarge, author of the 11 edition




The Cavum Septi Pellucidi Winter 10 Journal Of Ultrasound In Medicine Wiley Online Library




Agenesis Of Corpus Callosum Looking Through A Transducer




Normal Cns Anatomy Ob Images



Http Old Fygo Dk Files Ukursus 06 Ultrasound Q 05 Cns Definition Of planes Pdf




Dedicated To The Mission Of Bringing Free Or Low Cost Educational Materials And Information To The Global Ultrasound Community




Absence Of The Cavum Septum Pellucidum Iame




Fetal Brain Development In Small For Gestational Age Sga Fetuses And Normal Controls



Q Tbn And9gcqyfyjcuxxoqxupiyip L2y3vaysnxhvtv5hxex0ykypzqdod0p Usqp Cau



Www Isuog Org Uploads Assets Uploaded 9f5c6740 f6 41 9dca941bb98d0c Pdf



Cavum Septum Pellucidum And Vergae



Http Old Fygo Dk Files Ukursus 06 Ultrasound Q 05 Cns Definition Of planes Pdf




Fetal Central Nervous System Anomalies Chapter 6 Fetal Medicine




Dedicated To The Mission Of Bringing Free Or Low Cost Educational Materials And Information To The Global Ultrasound Community




Normal Cns Anatomy Ob Images



The Cavum Septi Pellucidi Myminifellowship




Columns Of The Fornix Not To Be Mistaken For The Cavum Septi Pellucidi On Prenatal Sonography Callen 08 Journal Of Ultrasound In Medicine Wiley Online Library



Www Ajronline Org Doi Pdf 10 2214 Ajr 17




Free Chapter Normal Fetal Ultrasound Biometry Ob Images




Agenesis Of The Corpus Callosum American Journal Of Obstetrics Gynecology



Www Ajronline Org Doi Pdf 10 2214 Ajr 17



Http Jdm Sagepub Com Content 23 6 336 Full Pdf Html




Case 321 Enlarged Fetal Cavum Septum Pellucidum Csp 34wk Youtube



Http Www Oyg Com Co Files The Cavum Septi Pellucidi Pdf




Absent Septum Pellucidum Radiology Reference Article Radiopaedia Org



Non Visualisation Of Cavum Septi Pellucidi Implication In Prenatal Diagnosis Insights Into Imaging Full Text




Fetal Imaging Williams Obstetrics 24th Edition



Fetal Brain Usg 1




Corpus Callosum And Septum Pellucidum Anomalies Radiology Key



Antenatal Diagnosis Of Corpus Callosal Agenesis Springerlink




Scielo Brasil Ultrasonographic Evaluation Of The Fetal Central Nervous System Review Of Guidelines Ultrasonographic Evaluation Of The Fetal Central Nervous System Review Of Guidelines




Normal Cns Anatomy Ob Images




Fetal Brain Development In Small For Gestational Age Sga Fetuses And Normal Controls




Abnormalities Of The Fetal Central Nervous System Prenatal Us Diagnosis With Postnatal Correlation Radiographics




Absence Of The Cavum Septum Pellucidum Iame
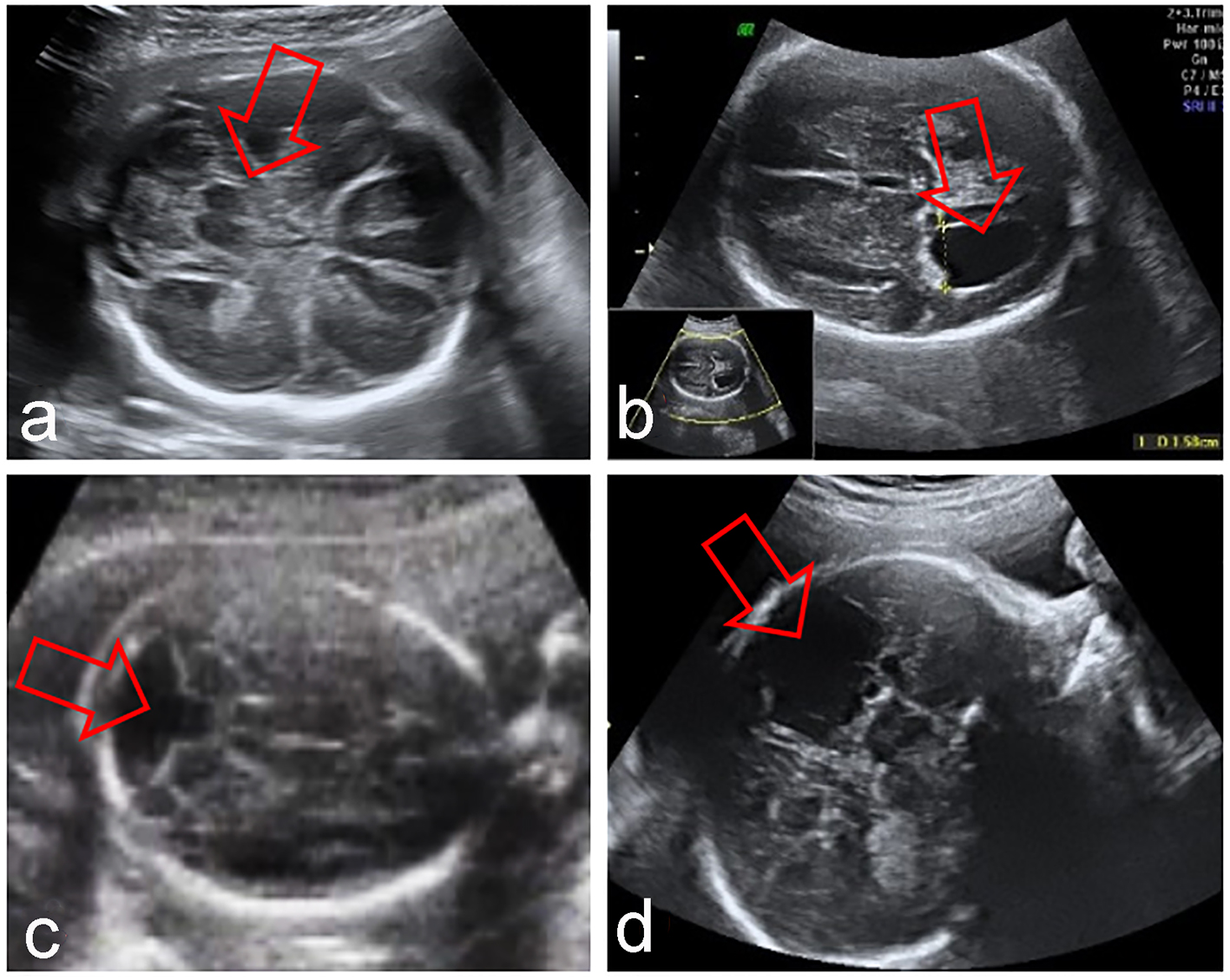



Outcome Of Fetuses With Abnormal Cavum Septi Pellucidi Experience Of A Tertiary Center Zorila Journal Of Clinical Gynecology And Obstetrics




Sod Plus Prenatal Ultrasound Revealed Non Visualisation Of Csp And Download Scientific Diagram




Dedicated To The Mission Of Bringing Free Or Low Cost Educational Materials And Information To The Global Ultrasound Community



Q Tbn And9gct8h38smzmvn Pev4iphq5u8fdqldmd 7fwm Buo0vtslqg44gi Usqp Cau




Absence Of The Cavum Septum Pellucidum Iame




Scielo Brasil Ultrasonographic Evaluation Of The Fetal Central Nervous System Review Of Guidelines Ultrasonographic Evaluation Of The Fetal Central Nervous System Review Of Guidelines



Www Ajronline Org Doi Pdf 10 2214 Ajr 17




Dedicated To The Mission Of Bringing Free Or Low Cost Educational Materials And Information To The Global Ultrasound Community



1




Corpus Callosum And Septum Pellucidum Anomalies Sciencedirect




Qpwfg2ahapdo4m




Absence Of The Cavum Septum Pellucidum Iame




Pdf Outcome Of Fetuses With Abnormal Cavum Septi Pellucidi Experience Of A Tertiary Center




The Cavum Septi Pellucidi Winter 10 Journal Of Ultrasound In Medicine Wiley Online Library



Onlinelibrary Wiley Com Doi Pdf 10 7863 Ultra 16




Figure 2 From Absent Cavum Septum Pellucidum A Review With Emphasis On Associated Commissural Abnormalities Semantic Scholar




Fetal Midline Anomalies Diagnosis And Counselling Part 1 Corpus Callosum Anomalies European Journal Of Paediatric Neurology



Http Webcir Org Revistavirtual Articulos 15 Septiembre Argentina Rar Anatomical Pdf




Prenatal Diagnosis Of Wagr Syndrome



Abnormalities Of Corpus Callosum




Scielo Brasil Ultrasonographic Evaluation Of The Fetal Central Nervous System Review Of Guidelines Ultrasonographic Evaluation Of The Fetal Central Nervous System Review Of Guidelines



Midline Anomalies Of The Brain




Dedicated To The Mission Of Bringing Free Or Low Cost Educational Materials And Information To The Global Ultrasound Community




Absence Of The Cavum Septum Pellucidum Iame




Corpus Callosum And Septum Pellucidum Anomalies Radiology Key



Cavum Septum Pellucidum And Vergae



Midline Anomalies Of The Brain




Corpus Callosum And Septum Pellucidum Anomalies Radiology Key




Absent Csp Ventriculomegaly Youtube



Journals Sagepub Com Doi Pdf 10 1177



Http Www Oyg Com Co Files The Cavum Septi Pellucidi Pdf
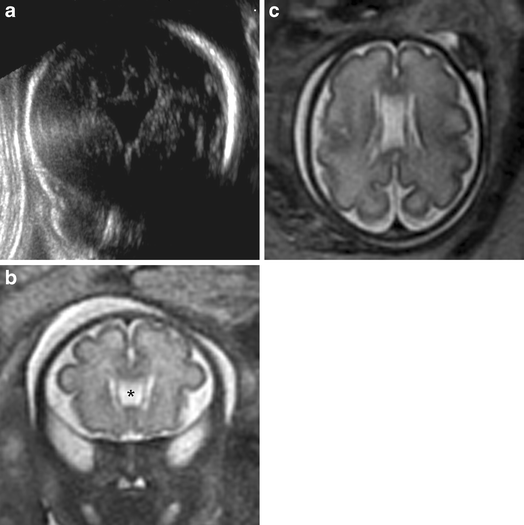



Non Visualisation Of Cavum Septi Pellucidi Implication In Prenatal Diagnosis Insights Into Imaging Full Text




Absent Cavum Septi Pellucidi American Journal Of Obstetrics Gynecology




Fetal Cns Abnormalities Associated To Absent Csp Syntelencephaly A Download Scientific Diagram



Www Isuog Org Uploads Assets 6a5d8e16 Adb7 4358 A308f65f1ab401 Final All Reading Materialweb Ready Pdf



Www Volusonclub Net Download A News B File C 511




The Cavum Septi Pellucidi Winter 10 Journal Of Ultrasound In Medicine Wiley Online Library




Normal Fetal Structural Ultrasound Obgyn Key



Q Tbn And9gcte4gf65dpaczis51z6ovwet0axshiud0irqpjchqmjo0nykztz Usqp Cau




Absent Cavum Septi Pellucidi American Journal Of Obstetrics Gynecology




Absence Of The Cavum Septum Pellucidum Iame



Midline Anomalies Of The Brain




Corpus Callosum And Septum Pellucidum Anomalies Sciencedirect
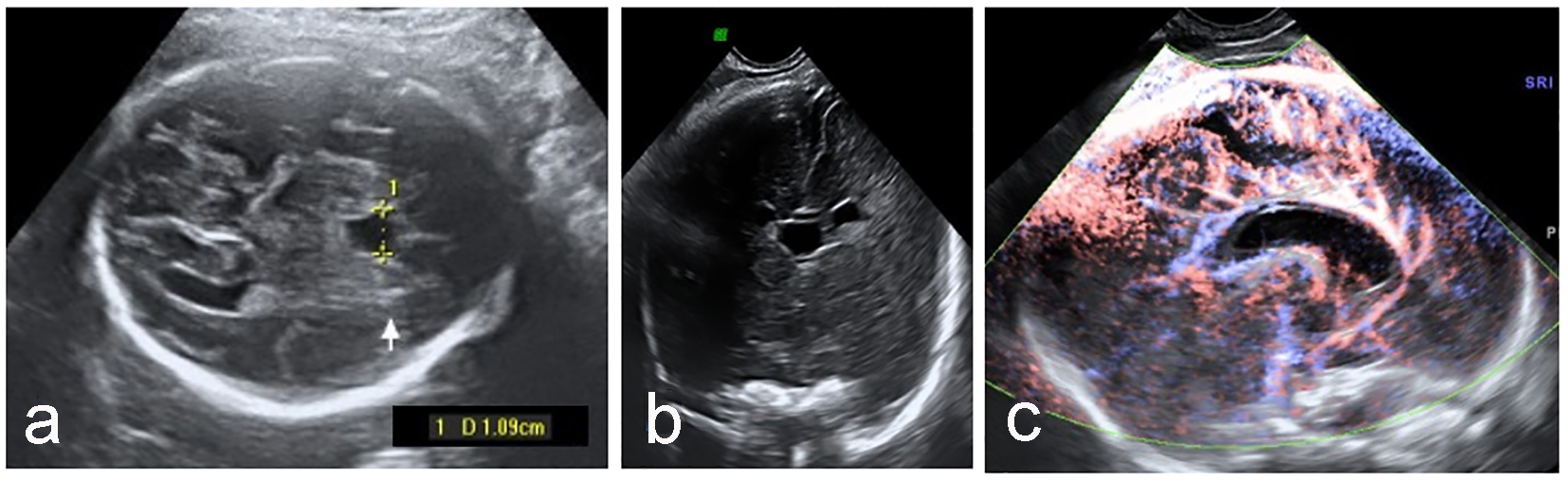



Outcome Of Fetuses With Abnormal Cavum Septi Pellucidi Experience Of A Tertiary Center Zorila Journal Of Clinical Gynecology And Obstetrics



Aucun commentaire:
Publier un commentaire